GLP-1 receptors (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 receptors) are a type of receptor that is part of the endocrine system, which plays a vital role in glucose metabolism and regulation.
These receptors are primarily found in several tissues throughout the body, including:
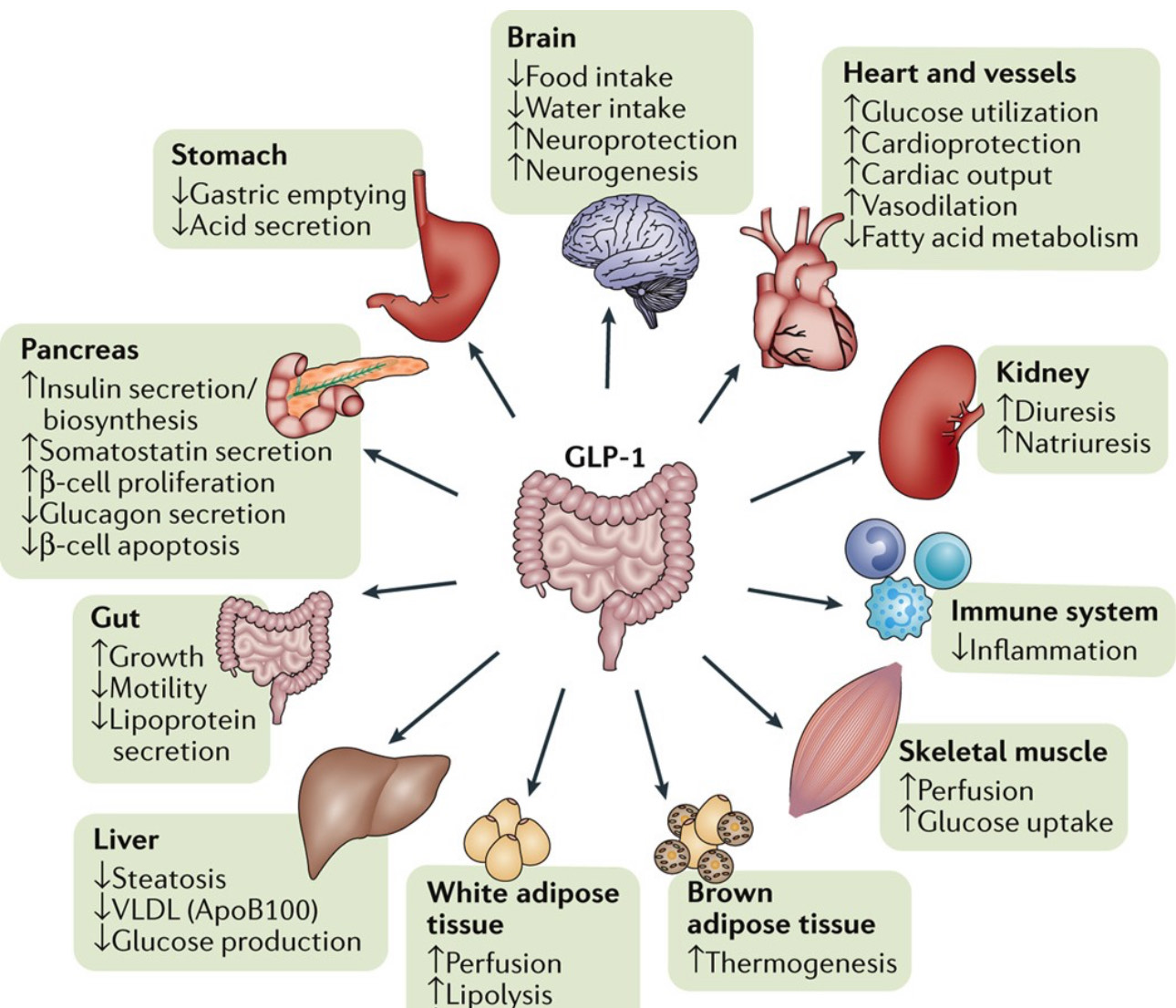
1. Pancreas: The highest concentration of GLP-1 receptors is located in the pancreas, where they are involved in stimulating insulin secretion in response to elevated blood glucose levels. They also help inhibit glucagon release, which reduces glucose production by the liver.
2. Gastrointestinal Tract: GLP-1 receptors are present in various parts of the gastrointestinal tract, where they influence gut motility and the secretion of digestive enzymes, ultimately contributing to the regulation of appetite and digestion.
3. Brain: GLP-1 receptors are found in specific areas of the brain, including the hypothalamus and brainstem. Activation of these receptors is associated with appetite suppression and the regulation of energy balance.
4. Heart: There is evidence that GLP-1 receptors are present in the heart and may play a role in cardiovascular function, including promoting cardiac health and reducing the risk of heart disease.
5. Kidneys: GLP-1 receptors are also found in the kidneys, where they may influence renal hemodynamics and sodium excretion.
What difference does all of this make for your health?
I'm glad you ask :)
Because GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) receptors are part of the endocrine system's regulatory mechanisms, particularly in relation to glucose metabolism and appetite control, GLP-1 hormone is secreted by the L-cells in the intestines in response to food intake. It plays and important roles in all of us because it:
1. Stimulates Insulin Secretion: GLP-1 enhances the secretion of insulin from the pancreas when blood glucose levels are elevated, which helps lower blood sugar levels.
2. Inhibits Glucagon Release: It suppresses the release of glucagon, a hormone that increases blood glucose levels, thereby contributing to glucose homeostasis.
3. Slowing Gastric Emptying: GLP-1 reduces the rate at which food leaves the stomach, which helps with satiety and regulates food intake.
4. Promotes Satiety: By acting on the brain, GLP-1 helps reduce appetite, which can aid in weight management.
In summary, GLP-1 receptors are important for all of us. Because of these roles, GLP-1 receptor agonists (synthetic drugs that mimic GLP-1) are used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. But WHAT IF you could support your body naturally? If you have tried GLP-1 receptors or are on the fence about them let's talk! I'd love to point you to resources that can provide support for you NO MATTER what you choose: agonists, natural support, or simply knowledge and awareness!
- lara@healthandlifecoachingllc.com
- Mon - Fri 9:00am to 5:00pm
Blog
Blog - Latest Articles
- Glucose Awakening May 4 - 31 04 April 2025
- Julia's story of hope and possibility! 21 February 2025
- Overwhelm and Burnout 21 February 2025
- Spring into Savings! 21 February 2025
- Cheating vs. Choice: A Perspective Shift for your Health Journey 07 February 2025
- Protein - SO MUCH MORE than Muscles! 22 January 2025
- GLP-1 Naturally 22 January 2025
- 4 Powerful Questions That Will Change Your Life 22 January 2025
- We are HOPE Givers! 22 January 2025
- Shrimp Scampi 22 January 2025
Services for You





Subscribe
Report
My comments